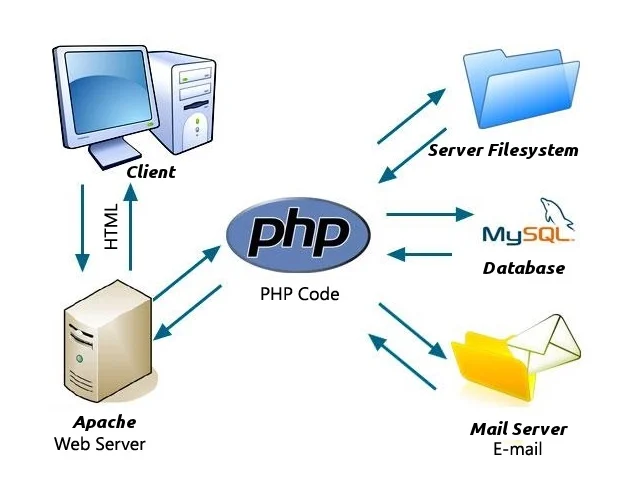
PHP, which stands for “Hypertext Preprocessor”, is a widely-used open-source scripting language especially suited for web development. It was created by Rasmus Lerdorf in 1994 and has grown into one of the most powerful server-side languages powering millions of websites and applications.
Unlike HTML, which only defines the structure of a web page, PHP allows developers to make pages dynamic—that is, responsive to user input and capable of interacting with databases, files, and other backend processes. This means PHP can generate content on the fly, manage sessions, handle forms, and even send emails automatically.
One of the reasons for PHP’s popularity is its simplicity. It’s easy for beginners to learn, yet robust enough for professionals to build complex web applications. PHP runs on almost every operating system and integrates well with popular databases like MySQL, PostgreSQL, and SQLite.
Over the years, PHP has evolved significantly. Modern PHP (versions 7 and 8) comes with enhanced performance, better security, and features like object-oriented programming and strong typing. Frameworks like Laravel, Symfony, and CodeIgniter have further improved how developers build scalable and maintainable web applications.
In fact, some of the world’s most popular platforms—including WordPress, Facebook (early versions), and Wikipedia—have used PHP as a foundation.
In short, PHP continues to be a reliable and flexible tool in the web developer’s toolkit, proving that even after decades, it’s still very much alive and evolving.


